Infertility
Infertility is the failure to conceive (regardless of cause) after 1 year of unprotected intercourse. This condition affects approximately 10-15% of reproductive-aged couples. In an over populated nation such as ours, the problem of infertility is still a major health problem. As per literature 1 out of every 16 couples are found to be infertile but incidence is increasing day by day.
Cause of Infertility
The various problems as late marriage, delayed child bearing, increased use of contraceptives and the medical disorders such as endometriosis, polycystic ovaries, genital tuberculosis, immunological disorders and male sub fertility have all contributed to this increased incidence especially in India.
Female and male factor of infertility
Female factors that affect fertility include the following categories:
- Cervical: Stenosis or Tightening or abnormalities of the mucus-sperm interaction
- Uterine: Congenital or acquired defects; may affect endometrium or myometrium; may be associated with primary infertility or with pregnancy wastage and premature delivery
- Ovarian: Alteration in the frequency and duration of the menstrual cycle—Failure to ovulate is the most common infertility problem
- Tubal: Abnormalities or damage to the fallopian tube; may be congenital or acquired
- Peritoneal: Anatomic defects or physiologic dysfunctions (eg, infection, adhesions, adnexal masses)
Male factors that affect fertility include the following categories:
- Pretesticular: Congenital or acquired diseases of the hypothalamus, pituitary, or peripheral organs that alter the hypothalamic-pituitary axis
- Testicular: Genetic or nongenetic
- Posttesticular: Congenital or acquired factors that disrupt normal transport of sperm through the ductal system
Factors that affect the fertility of both sexes include the following:
- Environmental/occupational factors
- Toxic effects related to tobacco, marijuana, or other drugs
- Excessive exercise
- Inadequate diet associated with extreme weight loss or gain
- Advanced age
Various common problems associated with infertility and their treatment:
- Male factor – Patients with low sperm counts or poor sperm motility often are treated with andrological evaluation with various tests as serum FSH, Prolactin, Testosterone, scrotal color Doppler and others. The treatment is given for 3-6 months. After 6 months, IUI for 3 cycles could be tried. However, the best and most successful treatment for most cases of sperm problems is ICSI.
- Blocked fallopian tubes: Hydrosalpinx (water filled in the tube) should be treated before proceeding with IVF.
- Endometriosis: Usuing laparoscopic surgery, enucleation and removal of chocolate cysts and pelvic adhesions is done. Thereafter, the couple may try naturally or can go for Intrauterine insemination. If this fails then IVF or ICSI can be tried.
- Unexplained Infertility: If no cause is found if infertility then two to three cycles of IUI followed by ICSI can be tried.
- Repeated IVF failures / Recurrent implantation failures / Recurrent miscarriages: The best options here are frozen embryo transfer with medications as high dose estrogen, vaginal sildenafil, aspirin and intrauterine instillation of Granulocyte Colony stimulating factor. If all these fail, we recommend intrauterine instillation of platelet rich plasma (PRP) can be tries.
- Poor ovarian reserve: The underlying problem is due to serum AMH level is low or there are very antral follicles seen on ultrasound indicating a low number of eggs. The medical treatment with an androgenisation protocol (combination of testosterone, letrozole, coenzyme Q, resveratrol and hCG ) followed by IVF can be tried.
Treatment of infertility
Medical treatments:
Medical treatment of infertility generally involves the use of fertility medication, medical device, surgery, or a combination of the following. If the sperm are of good quality and the mechanics of the woman’s reproductive structures are good (patent fallopian tubes, no adhesions or scarring), a course of ovulation induction maybe used. Medical treatment is directed toward suppressing estrogen production by the ovary. Different modalities of treatment are available. Depending on the therapeutic agent and the duration of treatment, endometriosis can be treated with oral contraceptives, progestins, androgens, or GnRH agonists. If conservative medical treatments fail to achieve a full term pregnancy, the doctor may suggest the patient undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF and related techniques (ICSI, ZIFT, GIFT) are called assisted reproductive technology (ART) techniques.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies:
Assisted reproductive technologies used to treat infertility include the following:
- Ovulation Induction
- In vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
- Zygote intrafallopian transfer ZIFT)
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- Sperm, oocyte, or embryo cryopreservation
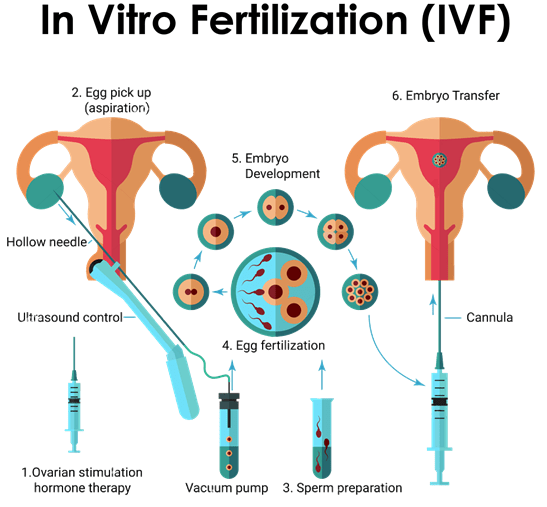

The brief details of the procedures is as under
- Ovulation induction: During this period we follow the growth of the follicles and the hormones they produce. If it is a stimulated cycle then a subcutaneous injection of Gonadotrophins administered daily for an average of 10-12 days. Depending on the stimulation protocol used, the duration might be longer and there might be an addition of a second injection for a few days. During the stimulation phase, usually 3-4 sonograms are needed to evaluate the size of the follicles and hormonal levels to evaluate what the follicles produce. The dose of the medications used is accordingly adjusted. When most of the follicles reach 17-20mm in diameter, an injection is administered to mature the oocytes and trigger the ovulation. The oocyte retrieval is scheduled 32-36 hrs later.
- Oocyte retrieval: In stimulated cycles where more than one oocyte needs to be retrieved, under short general anaesthesia the aspiration of the fluid of the follicles is done transvaginally with a hollow needle that is sonographically guided. At the other end of the needle there is a tube that is connected with a suction device that collects the aspirated fluid in specimen bottles. These are handed to the embryologists that identify the oocytes and count them in real time. After the procedure the patient is monitored for 1-2 hrs in order to make sure that everything is ok. Mild pain / discomfort in the lower abdomen can be expected that dissipates during the day.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI): This entails deposition of washed and capacitated sperm into the uterus at the time of spontaneous or induced ovulation. Several techniques are available for sperm washing such as layering, double spin or density gradients. The success rate with this procedure is in the lower range of 10 – 20% and generally 3 – 6 cycles are generally tried before proceeding to higher ART forms.
- In-vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET): This was called as test tube baby procedure where after controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with gonadotropins and follicles size of 18 mm, hCG is administered and the oocytes are aspirated at 36 hours post hCG (before they rupture) and transfered to the IVF laboratory. Here they are cultured in petri dishes containing culture medium. Subsequently, the oocytes are fertilized with the husband’s sperm after 4 – 6 hours of incubation. Indications for this procedure include tubal block, severe endometriosis and severe PCOD, unexplained infertility and infertility due to any cause refractory to conventional medical and surgical management. Success rates is in range of 30 – 40% per cycle and 3 – 5 cycles are recommended before opting for alternate treatment options.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): This technique is better than other methods and is especially indicated for male factor infertility which does not respond to conventional management. Males with severe oligo or asthenosoospermia are can still have their own child with this method. Patients Wife’s oocytes are aspirated and with special microscope with a micromanipulator, a single sperm is picked up in fine microneedle and injected manually into the oocyte. Embryos are transferred after 48 to 72 hours. The success rate is 30 – 40% chance of conception per cycle.
- Oocyte donation: Women who are menopausal or suffering from premature ovarian failure can still become pregnant with donated oocyte. Here, the uterus is prepared for conception with estrogen / progesterone priming. Once suitable oocytes are available, IVF is performed with the husband’s sperm and the embryos transfered to the recipient. Success rate is 60 %.This technique is also of immense value to patients with repeated IVF failures owing to poor ovarian reserve (low AMH or high FSH levels).
- Therapeutic insemination with donor sperm (TID): Patients suffering from severe male factor infertility who cannot afford ICSI or patients with primary testicular failure can opt for donor sperm from a semen bank. The success rate is 25% per cycle.
- Embryo donation: In the event of the wife being menopausal and the husband being azoospermic, the infertile couple can still hope for a pregnancy with embryo donation. The success rate with embryo donation is 70% in the presence of a normal endometrium.
- PGD/PGS (Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis/ Screening): The removal of one or more cells (embryo biopsy) from the developing embryo in the laboratory during an IVF cycle in order to do genetic tests. In the case of PGD we test for specific inherited diseases in order to clarify which embryos do not have the disease and only transfer the healthy ones back in the uterus. This is recommended to couples that are known to be carriers of a specific disease. In the case of PGS we screen in order to see which embryos have normal karyotype (number and size of chromosomes). These are the embryos that usually will result in a normal pregnancy. This technique is recommended when we have recurrent implantation failures despite a good number of embryos. The embryo biopsy is done at the day 5 or 6 stage (Blastocyst) and a few cells are removed from the trophectoderm part of the blastocyst, which is the part that is going to form the placenta in the future. Biopsy at the D3 stage or polar body biopsy have been abandoned since they are inferior in accuracy and have been shown to have detrimental effects on the embryos. The main disadvantage of the PGS technique is that it is still very expensive and this is why it is reserved for selected cases.
Important Counselling After Cycle Failure
Please Note that success rates in the best IVF centers in the world are in the range of 30 – 40% per started cycle. It is important for the patient to remember that the cumulative success rate after 3 cycles of IVF is in the range of 67%. This is an important statistic that highlights the need to do repeated cycles.
Dr. Sita Sharma is always available for counseling for the treatment of infertility. It is important to have this discussion to understand the gravity of the problem.
