Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
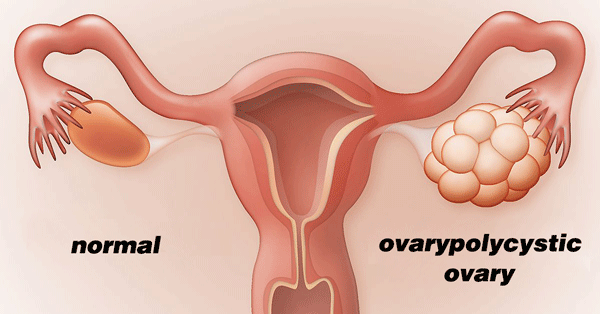
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce an abnormal amount of androgens, male sex hormones that are usually present in women in small amounts. The name polycystic ovary syndrome describes the numerous small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) that form in the ovaries. However, some women with this disorder do not have cysts, while some women without the disorder do develop cysts.
What causes PCOS?
The exact cause is not known but several factors may play a role in whether or not you develop PCOS. These include:
- Heredity: It may run in certain families so patient may be more prone to develop PCOS. It’s common for sisters or a mother and daughter to have PCOS.
- Hyperinsulinemia: Too much insulin and cause may be obesity and this can cause increased androgen production and difficulty ovulating.
- High levels of androgen: When ovaries produce too much androgen leading to hirsutism and acne. Women with PCOS have a type of low-grade inflammation that stimulates your ovaries to produce androgens.
What are the risks for PCOS?
The various risk factors are Obesity, Family history, High carbohydrate diet esp Burgers, Soft Drinks, fatty fried diets etc.
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
The symptoms of PCOS may include:
- Menstrual Irregularities, irregular periods, or very light periods
- Nonspecific pain lower abdomen due to large ovaries with cysts
- Excess body hair, including the face, chest, stomach, and back (hirsutism)
- Weight gain, especially around the belly (abdomen)
- Acne or oily skin
- Infertility
- Small pieces of excess skin on the neck or armpits (skin tags)
- Dark or thick skin areas of patches on the back of the neck, in the armpits, and under the breasts.
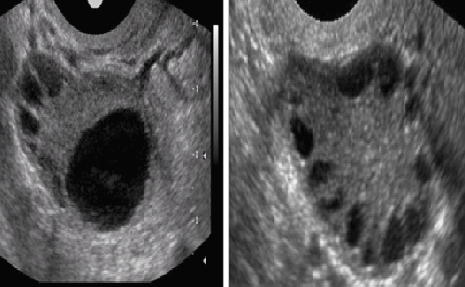

How is PCOS diagnosed?
This is diagnosed by symptoms and laboratory investigations including ultrasound of ovaries. There may be high levels of androgens and other hormones in blood with high blood sugar, cholesterol levels. There may be additional hypothyroidism
What are the complications of PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome can result in various complications as Infertility, Miscarriage or premature birth, liver fatty changes, facial hairs, Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders, Endometrial cancer, Obesity, Metabolic syndrome.
How is PCOS treated?
Treatment for PCOS depends on a number of modalities as:
- A change in diet and activity: A healthy diet and more physical activity can help you lose weight and reduce your symptoms. They can also help the body use insulin more efficiently, lower blood glucose levels, and may help to better ovulation.
- Incorporate good nutrition and regular physical activity. Losing weight can help the body to improve hormone levels. Even losing 10% of your body weight can make a difference in menstrual period and ovulation.
- Remove excess hair and slow down the future growth of your hair. Excess hair can be embarrassing. There are many facial hair removal techniques available, including creams, waxing, laser hair removal, and electrolysis. Laser hair removal and electrolysis must also be performed by a qualified professional.
- Medications to cause ovulation. Medications can help the ovaries to release eggs normally. These medications also have certain risks. They can increase the chance for a multiple birth (twins or more). And they can cause ovarian hyperstimulation. This is when the ovaries release too many hormones. It can cause symptoms such as abdominal bloating and pelvic pain.
- This medication improves your body’s ability to lower blood sugar, insulin, and androgen levels. Metformin can help restart your ovulation, and may even help you lose weight and improve cholesterol levels.
- Hormonal birth control. If you don’t want to get pregnant, birth control can help regulate your menstrual cycle, lower your risk of endometrial cancer, improve acne, and reduce extra facial hair.
- Anti-androgen medicines. Because anti-androgen medicines reduce androgens in your system, they can reduce hair loss on your scalp, reduce facial and body hair growth, and improve acne. Don’t take these medications during pregnancy.
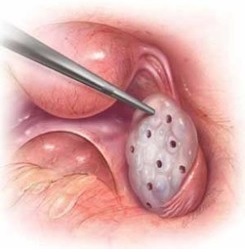
- Surgical Treatment for PCOS: Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling can be done in some cases.